一、双指针
双指针是指使用两个指针对线性数据结构进行遍历/搜索的方法。 双指针方法包括:
- 首尾指针
- 快慢指针
- 前后指针
二、双指针方法解析
首尾指针
首指针从线性表从前往后遍历,尾指针从线性表尾部往前遍历。
[剑指offer-57] 和为s的数字
输入一个递增排序的数组和一个数字s,在数组中查找两个数,使得他们的和正好是s。 如果有多对数字的和等于s,则输出任意一对即可。 如:输入数组[1, 2, 4, 7, 11, 15]和数字15,由于4 + 11 = 15,则输出[4, 11]即可
采用首尾指针的双指针方法,如图所示: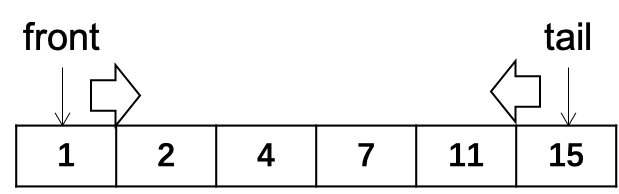
- 若nums[front] + nums[tail] < s, 则说明nums[front]太小了,需要增大,故front++;
- 若nums[front] + nums[tail] > s,则说明nums[tail]太大了,需要减小,故tail--;
- 若nums[front] + nums[tail] == s,得到解;
- 结束条件front >= tail,无解
int target_sum(int *nums, int nums_size, int target, int *ret_array)
{
int front = 0;
int tail = nums_size - 1;
if ((!nums) || (!ret_array) || (nums_size < 2)) {
return -1;
}
while (front < tail) {
if ((nums[front] + nums[tail]) == target) {
/* find the solution */
ret_array[0] = nums[front];
ret_array[1] = nums[tail];
break;
}
if ((nums[front] + nums[tail]) < target) {
/* increase left part */
front++;
} else if((nums[front] + nums[tail]) > target) {
/* decrease left part */
tail--;
}
}
return (front < tail) ? 0 : -1;
}
对于上述方法,由于最多遍历整个数组的所有元素,故时间复杂度是O(n)。
如果数组是没有排序的,且可以改变数组,则可以先qsort()排序,然后再用首尾指针。
同理,对于三数之和的题目[leetcode-15],
就可以排序,然后固定一个数,然后就是上述的两数之和了,这样的话,可以在O(n^2)
的时间复杂度内解决。
前后指针
前指针先走k步,然后前后指针同步往后遍历。
[剑指offer-22] 链表中倒数第k个节点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。如1->2->3->4->5->6,则倒数第3个节点 就是4所在的节点。
采用前后指针方法,如图所示: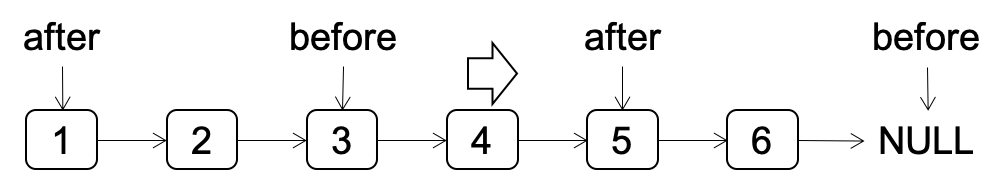
- 前指针先走k步
- 前后指针一起走,直到前指针走到NULL
- 此时后指针指向的节点就是链表的倒数第k个节点
- 注意:如果链表长度小于k,该如何处理
struct list_node *find_last_kth_node(struct list_node *head, int k)
{
int step = 0;
struct list_node *before = head;
struct list_node *after = head;
/* before pointer move k step */
for (step = 0; step < k; step++) {
if (!before) {
break;
}
before = before->next;
}
/* list length < k */
if ((!before) && (step < k)) {
return NULL;
}
/* traverse until before is NULL */
while (before) {
before = before->next;
after = after->next;
}
return after;
}
从前指针的角度看,前指针从链表头遍历一遍到链表尾,故时间复杂度为O(n)。
类似的题目如删除链表倒数第N个节点[leetcode-19],
需要注意的是,删除节点需要另外考虑头节点/中间节点/尾节点删除之后,节点之间指针的变化。
快慢指针
顾名思义,就是双指针中一个指针快一个指针慢,通常都是让快指针一次走2步,慢指针一次走1步。
[剑指offer-23] 链表中环的入口节点
如果链表中包含环,如何找出环的入口节点?如图所示,环的入口点为4的节点。
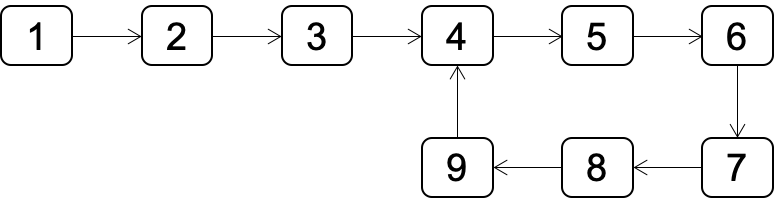
此问题分为如何判断是否有环?和有环的情况下,如何得到环的入口点。两个子问题。
如何判断有环?
这里就要使用快慢指针。我们想象,两个同学以不同的速度,同时从教室跑到操场,
然后开始绕操场跑圈。
如果操场是直线的操场,那么跑得快的永远都在前面,直到尽头。
如果操场是圆圈的操场,那么跑得慢的同学和跑得快的同学总会相遇,而且肯定是在操场上相遇。
回到题目中,我们就可以这样来判断链表中是否有环:
- 快指针一次走2步,慢指针一次走1步,两个同时从头指针处开始走
- 如果快指针走到了NULL,那说明没有环
- 如果快指针与慢指针再次相遇了,说明存在环
struct list_node *list_contain_circle(struct list_node *head)
{
struct list_node *fast = head;
struct list_node *slow = head;
/* fast move 2 step each time, slow move 1 step each time */
for (;;) {
/* fast pointer will goto NULL, no circle */
if ((fast->next == NULL) || (fast->next->next == NULL)) {
return NULL;
}
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
/* fast pointer equal to slow, circle
* put check after fast and slow update, as fast and slow are both
* initialized to head, this is their meet again.
*/
if (fast == slow) {
return fast;
}
}
}
如何得到环的入口点
前面我们判断出链表是否存在环,假如存在环,且环的大小是n。那么我们通过前后指针,
让前指针先走n步,然后前后指针一起走,当前后指针相遇的时候就是环的入口点。
这里可以这样理解,你和同学从教室跑去绕操场,你同学一直在领先你一圈的位置。
那么,当你跑到操场入口的时候,你同学在你前面一圈的位置,也就是刚好也在操场入口。
- 求出环的长度n,只需要从环上一点,开始循环计数,直到回到原点,即得环长度
- 前指针走n步,前后指针一起走,直到前后指针重叠
- 返回此时前后指针的节点,即为环的入口点
/* node in the circle can be get from the list_contain_circle interface. */
int list_circle_length(struct list_node *circle_node)
{
int circle_len = 0;
struct list_node *curr = circle_node->next;
while (curr != circle_node) {
circle_len++;
curr = curr->next;
}
return circle_len + 1;
}
struct list_node *list_circle_entry(struct list_node *head)
{
struct list_node *before = head;
struct list_node *after = head;
struct list_node *node_in_circle = list_contain_circle(head);
int circle_len = 0;
int step = 0;
if (!node_in_circle) {
return NULL;
}
circle_len = list_circle_length(node_in_circle);
/* before pointer move circle_len step */
for (step = 0; step < circle_len; step++) {
before = before->next;
}
/* move together */
while (before != after) {
before = before->next;
after = after->next;
}
return before;
}
可以看到,在判断是否有环时遍历了一遍链表,在计算环长度遍历了环, 最后查找入口节点时最多可能遍历一边链表。因此,时间复杂度在O(n)量级。
三、总结
在数组中使用双指针,通常需要是排序的数组,因此,对没有排序的数组可以先对数组进行排序。
如前面提到的三数之和的题目[leetcode-15]。
数组中双指针进一步可能拓展到多指针,如leetcode-632
最小区间问题。
双指针也会用在字符串中,如leetcode-76最小覆盖字串。